
The Fur Trade Storyboard by 2f1e4e24
Fur Trade Timeline. In this lesson, students will play a class game of "I Have. Who Has?" and create a timeline for Canada's fur trade. Created by Elizabeth Phipps 2012 recipient of the Governor General's History Award for Excellence in Teaching. This lesson is inspired by the article "Fur Trade Times" in the How Furs Built Canada.

fur trade Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
classroom. The purpose of the game is to demonstrate elements of the fur trade era and the people involved in the fur trade in a fun and easy to learn way. The game showcases the material culture of the different key groups (First Nations, Métis and Euro-anadian trading companies) involved in the fur trade. It is a collaborative, strategy.
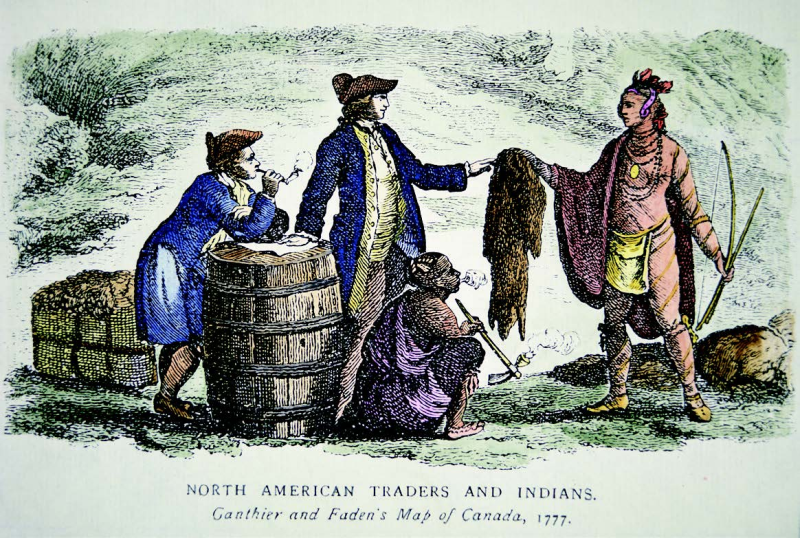

Image Fur Traders American Horizons 3e Dashboard Resources
The fur trade was a thriving industry in North America from the 16th through 19th centuries. When Europeans first settled in North America, they traded with Indigenous peoples (known in different places as First Nations, Native Americans, or American Indians). The Indigenous people often gave the settlers animal furs in exchange for weapons.

HandsOn Canadian History The Fur Trade Game Fur trade, Canadian
Fur Trade Educational Package. Download the PDF. When we talk about the fur trade, we mean a time starting in the late 1600s when companies based in Europe spread throughout what is now Canada. They traded with Indigenous people for animal fur, mostly from beavers but from other animals, too. The Hudson's Bay Company, often called HBC, is one.

5 phases of the fur trade Storyboard by 2dd67828
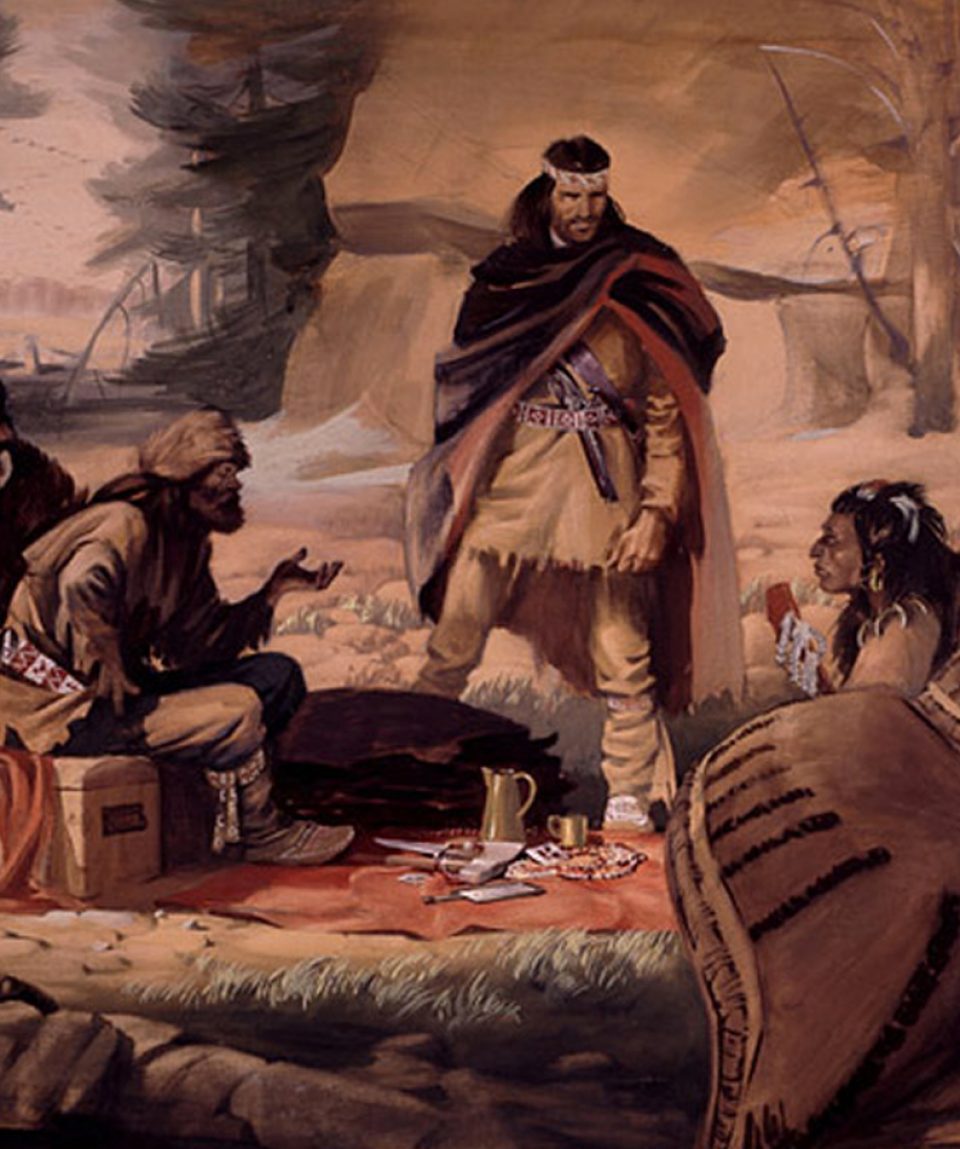
Trappers, Traders & Pathfinders. While the Government was neglecting the western country of the Plains, private enterprise had been slowly prying open its secrets, and individuals were finding their uncertain way along its watercourses or across its sun-browned prairie. The fur trade was the powerful magnet that thus early drew westward hardy.

Djordje Todorovic Illustrator Fur Trade Game Pieces
In this lesson, students will hear a story about life as a voyageur's family during the Fur Trade. The students will then play the Fur Trade Game (like an Easter egg hunt) where they collect furs to trade for items from a "trading post". The students will complete a "Fur Trader's Log Book". Time Required: 50 minute period

Fur Trade Educational Package Canada's History Fur trade, History
As the 2020 Lieutenant Governor of Saskatchewan Heritage Awards have been cancelled due to COVID-19, we have been catching up with past winners throughout the month of October. In 2019, the Saskatchewan Archaeological Society (SAS) took home the Public Outreach award for, "Trappers and Traders: A Fur Trade Card Game.".
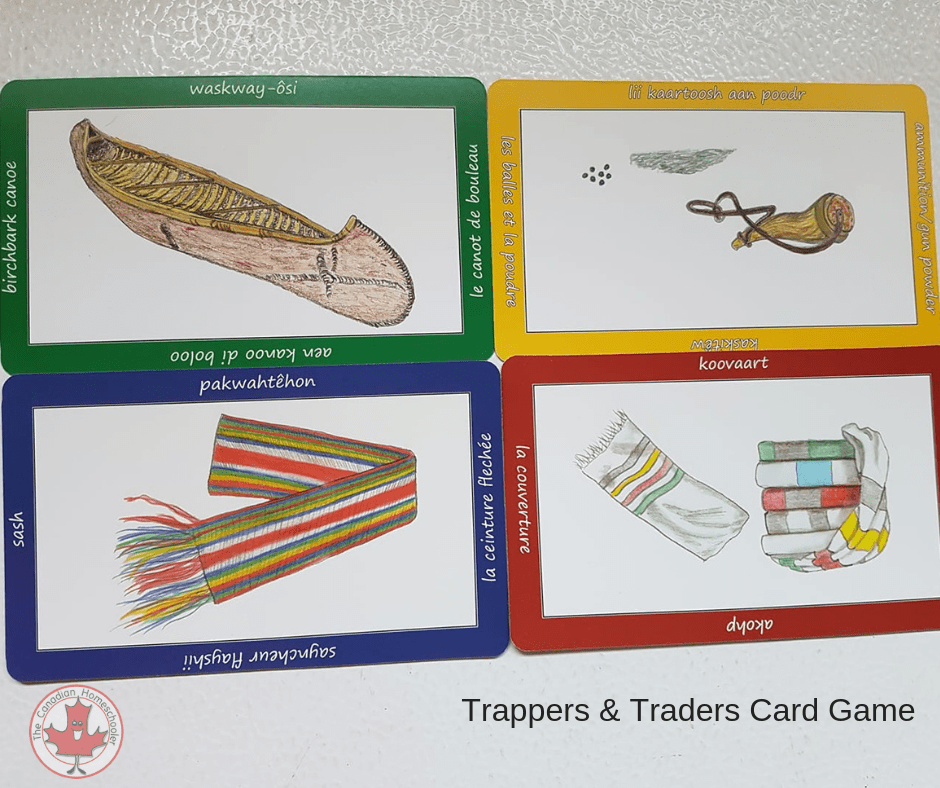
Trappers and Traders A Fur Trade Game {Review}
Recently I overheard a group of fourth graders using the fur trade SEND trunk exclaim with excitement, "Hey, it's just like Minecraft!". For those of you not familiar with the phenomenon of Minecraft, it is one of the most popular video games in the world having sold more than 60 million copies as of October 2014. Minecraft Landscape.

HandsOn Canadian History The Fur Trade Game
Game Description. The material culture of four different groups involved in the fur trade, First Nations, Métis, the Hudson Bay Company, and the Northwest Company is showcased in the game. Students are divided into four groups representing each one of these groups. Each group is given a list of items they need to trade for, and 21 trading.

Trappers and Traders A Fur Trade Game {Review}
The Fur Trade Era: A Trade Game. Student will learn and categorize the many contributions that American Indian (specifically Anishinaabe) have made to all aspects of modern society during the fur trade era. Ojibwe Language will be integrated through basic vocabulary that was used during the trading era. Materials Needed Resources

Trappers and Traders A Fur Trade Game {Review}
The fur trade changed the economy of First Nations, because as well as hunting and trapping for subsistence, First Nations people were now trapping to acquire trade goods. Unlike New France, the Hudson's Bay Company did not create British colonies, but brought in many employees from Ireland and the Orkney Islands off Scotland with contracts to.

Trappers and Traders A Fur Trade Card Game Saskatchewan
In this lesson, students will learn about life as a voyageur's family during the Fur Trade and then will play the Fur Trade Game where they collect "furs" to trade for items from a "trading post.". Created by Elizabeth Phipps 2012 recipient of the Governor General's History Award for Excellence in Teaching. This lesson is inspired.

Fur Trade Worksheets Grade 5 Esl Math Worksheets Pdf
The Fur Trade Game 3 or more players . The Fur Trade Game is designed to simulate the activities of a trading post with players acting as the traders/trappers. Players will search for Made Beaver Units and trade them in at the trading post station for trade items needed for survival..

Coureursdebois Fur Trade Game Bark Lake Leadership and Conference
A fur trader in Fort Chipewyan, Northwest Territories in the 1890s A fur shop in Tallinn, Estonia in 2019 Fur muff manufacturer's 1949 advertisement. The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur.Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued.

Trappers and Traders A Fur Trade Card Game Saskatchewan
This interactive, multi-player game attempts to bring the experience of the fur trading days to life. Inside the box are 4 sets of colour-coded cards along with matching paper pads. The colours represent four different groups: Hudson' Bay Company, North West Company, a First Nations Trading Party, and a Metis Trading Party. The cards.

Fur Trade Scavenger Hunt Game
Fur Trade in Canada. The fur trade was a vast commercial enterprise across the wild, forested expanse of what is now Canada. It was at its peak for nearly 250 years, from the early 17th to the mid-19th centuries. It was sustained primarily by the trapping of beavers to satisfy the European demand for felt hats.