
The First Victims of the First Crusade The New York Times
Major Events: Albigensian Crusade Battle of Ḥaṭṭīn Siege of Edessa

The First Crusade Causes and Effects Video & Lesson Transcript
People who went on the Crusades were motivated by different reasons including the prospect of wealth, freedom or power. Key figures involved in the Crusades included Richard the Lionheart and.
38 Curious Facts About The Crusades
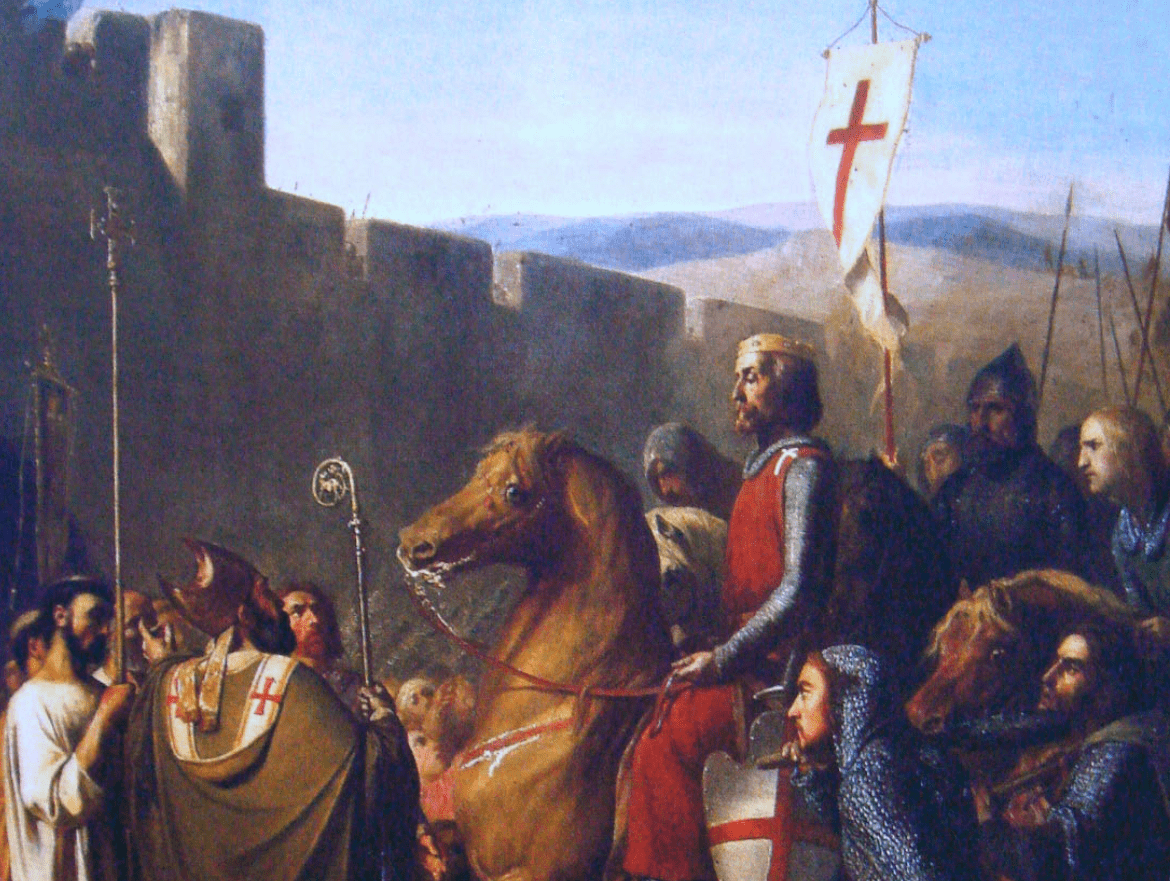
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica The Crusades were organized by western European Christians after centuries of Muslim wars of expansion. Their primary objectives were to stop the expansion of Muslim states, to reclaim for Christianity the Holy Land in the Middle East, and to recapture territories that had formerly been Christian.

Map Of The Four Crusades Stock Illustration Download Image Now Map, Byzantine, Islam iStock
Territorial expansion Second, crusading played a major role in European territorial expansion. The First Crusade resulted in the formation of the crusader states in the Levant (the eastern Mediterranean), which were initially governed, and in small part populated, by settlers from Europe.

The First Crusade OCR B GCSE History 91 Lesson Resources
Terminology The Siege of Damascus (1148) as depicted in the Passages d'outremer, c. 1490 The term "crusade" first referred to military expeditions undertaken by European Christians in the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries to the Holy Land.
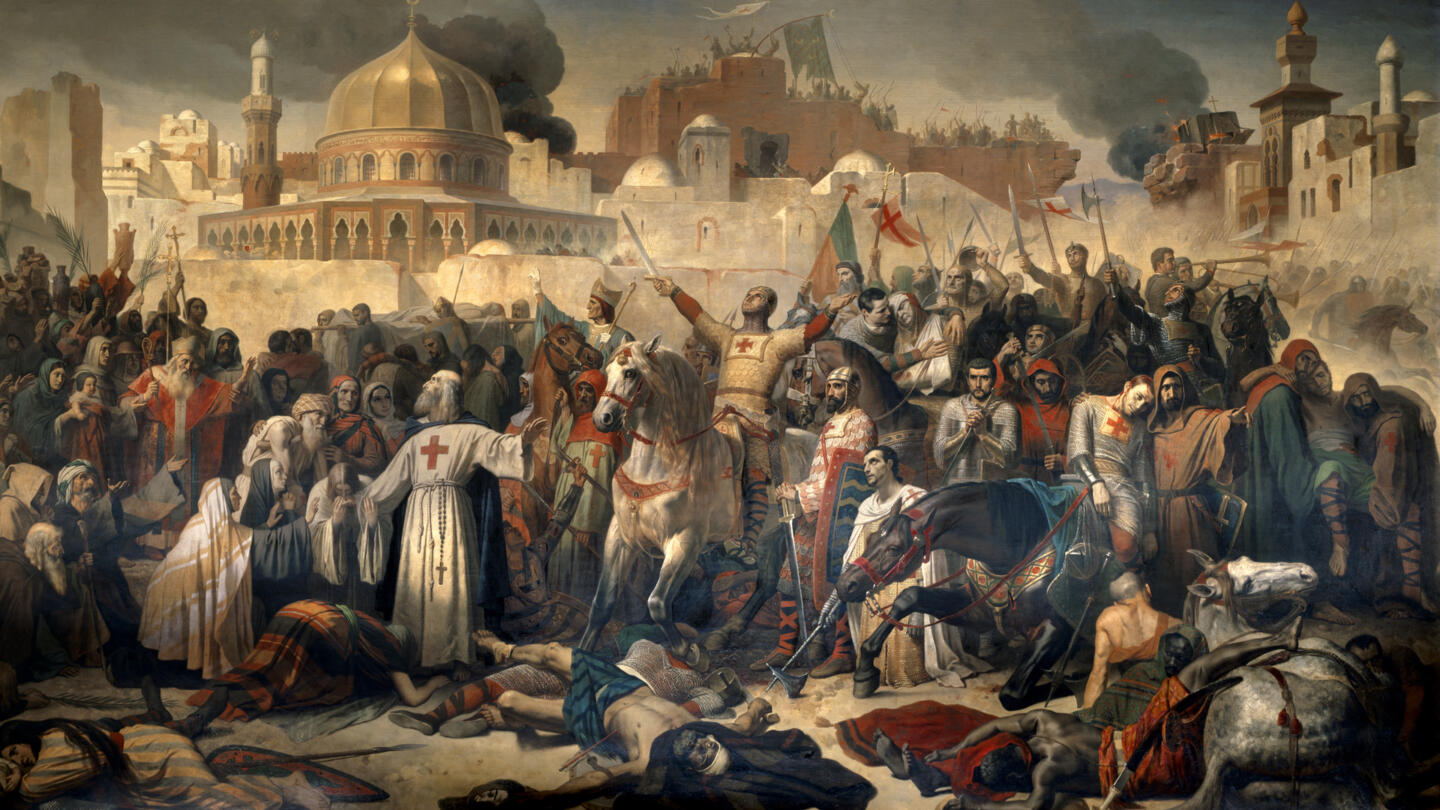

The Templars' Crusader Origins HISTORY
Below is the article summary. For the full article, see Crusades . Crusades, Military expeditions, beginning in the late 11th century, that were organized by Western Christians in response to centuries of Muslim wars of expansion.

The Crusades Facts, Worksheets & Summary Of 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th & 5th
Crusade as metaphor One of the most enduring though least-discussed results of the Crusades was the development of the word crusade (which first appeared in its Latin form in the late 12th or early 13th century) to denote any common endeavour in a worthy cause.
The Crusades Facts, Worksheets & Summary Of 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th & 5th
Holy Land . His lord is persuaded, and gathers his men and resources. The man-at-arms says goodbye to his family, and departs in 1096 on years of painful journeying and military campaigns. He dies of starvation at Antioch, never seeing Jerusalem. His family never knows his fate. This was crusading.

Crusades Definition, History, Map, Significance, & Legacy Britannica
Article by Mark Cartwright published on 04 July 2018 Listen to this article Available in other languages: Arabic, French, Greek, Portuguese, Spanish, Turkish The Crusades were a series of military campaigns organised by Christian powers in order to retake Jerusalem and the Holy Land back from Muslim control.

The Crusades by Roy Parton
Most historians consider the sermon preached by Pope Urban II at Clermont-Ferrand in November 1095 to have been the spark that fueled a wave of military campaigns to wrest the Holy Land from Muslim control. Considered at the time to be divinely sanctioned, these campaigns, involving often ruthless battles, are known as the Crusades.
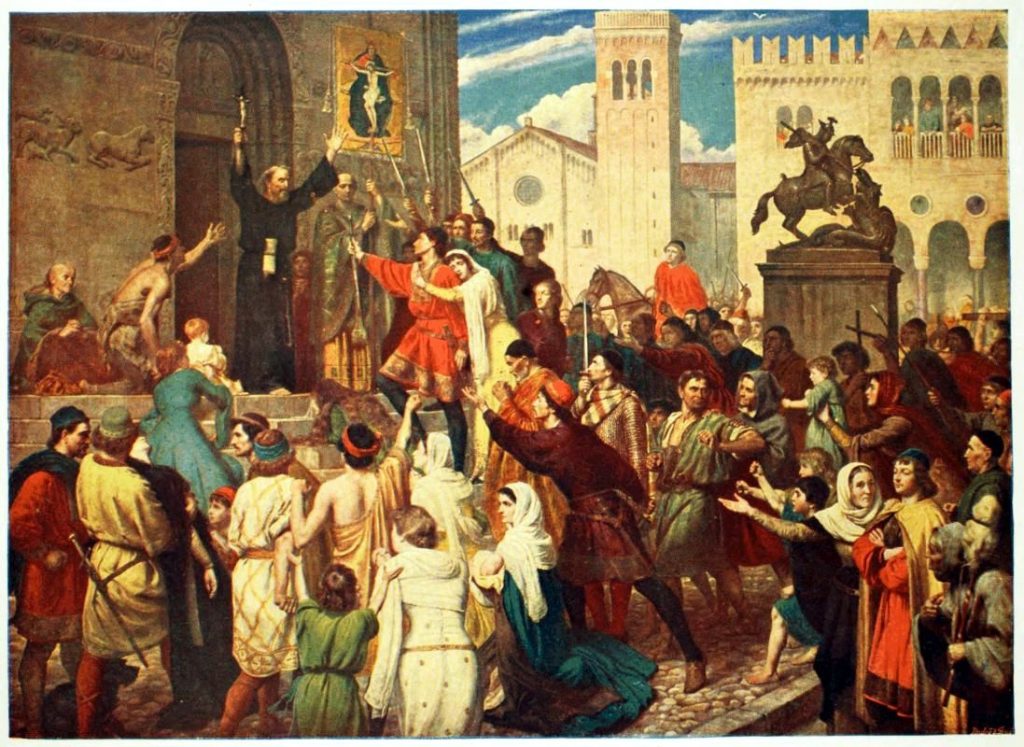

The Crusades Motivations, Administration, and Cultural Influence Brewminate A Bold Blend of
The Crusades were a series of invasions of the Middle East by Europeans in the name of Christianity. They went on, periodically, for centuries. They resulted in a shift in the identity of Latin Christianity, great financial benefits to certain parts of Europe, and many instances of horrific carnage. The Crusades serve as one of the iconic.

The Crusades Facts, Worksheets & Summary Of 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th & 5th
Crusades, military expeditions, beginning in the late 11th century, that were organized by western European Christians in response to centuries of Muslim wars of expansion. The Crusades took place from 1095 until the 16th century, when the advent of Protestantism led to the decline of papal authority.

The Crusades by 1351
Through the use of a broader range of evidence than ever before (especially charters, that is sales or loans of lands and/or rights), a stress on contemporary religious impulses as the dominant driver for, particularly the First Crusade, came through.

Eduqas GCSE History 1E. The Crusades, c10951149 History Resources
Muslim forces ultimately expelled the European Christians who invaded the eastern Mediterranean repeatedly in the 12th and 13th centuries—and thwarted their effort to regain control of sacred Holy.

Did the Crusades lead to Islamic State? The University of Sydney
SECTION 15The Crusades and Medieval Christianity. Spanning most of the High Middle Ages (1050-1300 CE), a series of military expeditions called the Crusades was launched from Christian Europe against the peoples of the Near East. Sparked by a zeal to rid the Holy Lands of "infidels"—meaning Moslems primarily—only the First Crusade achieved.

The Crusades by Roy Parton
0:46 Introduction In wars called the Crusades, Christians from Europe fought Muslims for control of Jerusalem and other holy places. The word crusade comes from the Latin word crux, meaning "cross." The Christian soldiers, called Crusaders, wore the cross as a symbol of their religion. The Crusades took place between 1095 and 1291.